啰音
所谓的啰音是呼吸音以外的附加音,该音正常情况下并不存在,故属于非呼吸音的改变,按性质的不同可分为下列几种。

湿性啰音
1.大水泡音(粗湿啰音)
2.中水泡音(中湿啰音)
3.小水泡音(细湿啰音)
4.捻发音
干性啰音
1.高调干啰音
2.低调干啰音
(一)湿性啰音
1.概念及发生机制
系由于吸气时气流通过呼吸道内的分泌物如渗出液、痰液、血液、黏液和脓液等,形成的水泡破裂所产生的声音,故又称水泡音。
常见于支气管病变、感染性肺部炎症、肺水肿、肺泡出血。

看气道内水泡的形成与破裂
2.听诊特点

湿啰音听诊特点
1.湿啰音是呼吸音外的附加音,为断续短暂的水泡破裂声,一次常连续多个出现。
2.大、中、小水泡音的形成与其所在管腔径的大小相一致。
3.吸气时或呼气终末较为明显,有时可出现于呼气早期。
4.部位较恒定,性质不易变。
5.中、小湿啰音可同时存在,咳嗽后可减轻或消失。
3.分类及特点
(1)大水泡音(粗湿啰音)

听诊特点
>>产生部位:气管、主支气管或空洞部位。
>>出现时期:多出现在吸气的早期。
>>临床意义:可见于
①支气管扩张
②严重肺水肿
③肺结核空洞

大水泡音(粗湿啰音)

请听
(2)中水泡音(中湿啰音)
听诊特点
>>产生部位:发生于中等大小的支气管。
>>出现时期:多出现在吸气的中期。
>>临床意义:可见于
①支气管炎
②支气管肺炎

中水泡音(中湿啰音)

请听
(3)小水泡音(细湿啰音)
听诊特点
>>产生部位:发生于小的支气管。
>>出现时期:多出现在吸气的后期。
>>临床意义:可见于
①细支气管炎
②支气管肺炎、肺淤血和肺梗塞等
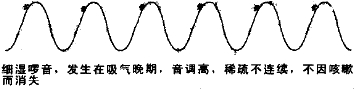
小水泡音(细湿啰音)

请听
(4)捻发音
听诊特点
>>发生机制:肺泡壁相互粘着陷闭所致。
>>出现时期:多出现在吸气的后期。
>>临床意义:可见于
①细支气管炎
②肺泡炎症
③肺淤血
④肺炎早期等
捻发音

请听
(二)干性啰音
1.概念及发生机制
干性啰音是由于气道狭窄或部分阻塞,气体通过时产生湍流所发出的声音。常见于气道炎症充血水肿、平滑肌痉挛、管腔内外肿瘤压迫等。

2.听诊特点
湿啰音听诊特点
1.是一种持续时间较长,音调较高,带乐音性质的呼吸附加音。
2.吸气与呼气均能听到,但以呼气时明显。
3.干啰音的强度和性质易改变,部位易变换,在瞬间内数量可明显增减,咳嗽后可消失。
3.分类及特点
(1)高调干啰音(飞箭音、鸟鸣音、哨笛音、哮鸣音等)
听诊特点
>>产生部位:较小的支气管或细支气管。
>>出现时期:吸气、呼气均有,但呼气时明显。
>>声音特点:持续时间长、调高、乐音性质。
>>临床意义:可见于
①弥散性:支气管哮喘、心源性哮喘、慢支等
②局限性:支气管内膜结核、肺癌、气管异物

飞箭音
呼气相哮鸣音
请听
鸟鸣音

呼气相哮鸣音
请听
哨笛音
双相哮鸣音
请听
哮鸣音
呼气相哮鸣音
请听
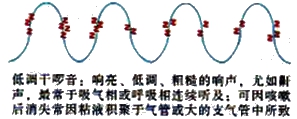
(2)低调干啰音(鼾音)
听诊特点
>>产生部位:气管或主支气管
>>出现时期:常出现在呼气相或呼吸相连续
>>声音特点:响亮、低调、粗糙的干啰音
>>临床意义:可见于急、慢性支气管炎
鼾 音

请听
【医教育网原创,转载请注明出处!违者必究!!!】